Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 검색어 추천
- 백준
- ai agent
- 결제서비스
- 카카오
- docker
- 베타적락
- piplining
- 아키텍쳐 개선
- jwt 표준
- spring event
- 셀러리
- 누적합
- 디버깅
- gRPC
- ipo 매매자동화
- BFS
- 크롤링
- langgraph
- AWS
- 추천 검색 기능
- 레디스 동시성
- 이분탐색
- 몽고 인덱스
- 쿠키
- JPA
- 구현
- 완전탐색
- next-stock
- 프로그래머스
Archives
- Today
- Total
코딩관계론
[프로그래머스] 아이템 줍기 본문
반응형
문제 이해하기
주어진 지형에서 아이템을 줍기위한 최단 거리를 구해야 한다.
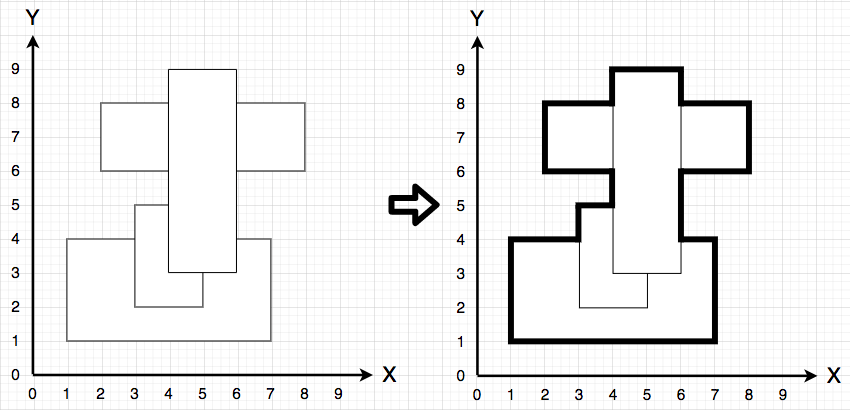
제한사항은 가장 바깥쪽 테투리만을 이용해 캐릭터를 이동시켜야 한다는 점이다.
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/87694
문제 해결 방법
1. 배열의 크기를 두 배 늘려야합니다.
아래의 사진을 보시면 5, 3에서 6, 3으로 바로 접근을 할 수 없습니다.하지만 배열의 탐색에서는 인접인덱스끼리의 접근이 가능함으로 오답이 나오게 됩니다.따라서 기존 5, 3이 아닌 크기를 두 배를 늘린 배열을 사용해야 합니다. 따라서 해당 좌표는 (10, 6), (12, 6)으로 변경되고, 직접 접근할 수 없게 됩니다.
또한 기본적인 좌표와 배열의 좌표 표현 방식이 달라지면서 그림과 똑같이 맞추기 위해서 정규화를 진행했습니다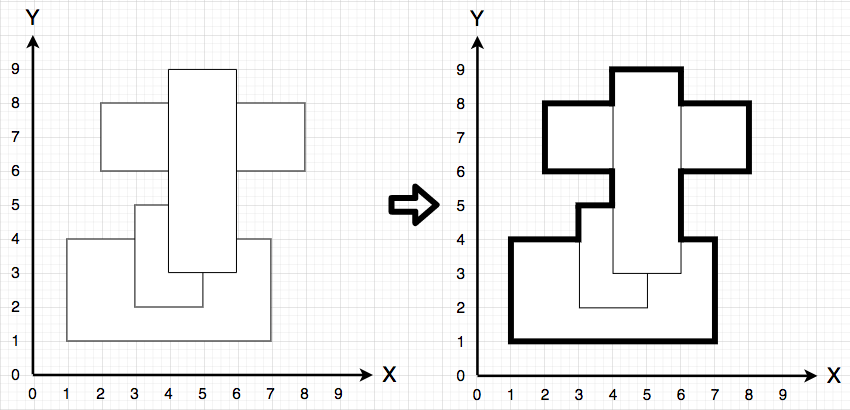
for i in range(len(rectangle)):
rectangle[i][0] = rectangle[i][0]*2
rectangle[i][1] = 100 - (rectangle[i][1]*2) #정규화
rectangle[i][2] = rectangle[i][2]*2
rectangle[i][3] = 100 - (rectangle[i][3]*2)
2. 좌표기 사각형 테두리인지, 내부에 위치하는지 판별해야합니다.
사각형의 최외각 좌표들을 안다면 해당 좌표가 사각형의 내부에 위치했는지, 외부에 위치했는지 쉽게 판별할 수 있습니다.
왜냐하면 사각형의 내부에 위치해있다면 필연적으로 최외각점들보다 작을 수 밖에 없습니다. 코드로 표현하면 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있습니다.
def is_outline(x, y, rocks):
for rock in rocks:
y1, x1, y2, x2 = rock
#정규화로 인함
if x2 < x < x1 and y1 < y < y2:
return False
return True
3. 최단 거리를 구해야합니다.
최단거리는 bfs를 통해서 구할 수 있습니다.
def bfs(board, x, y, rocks):
queue = []
scoure_board = [[987654321] * 101 for _ in range(101)]
heapq.heappush(queue, (0, x, y))
while queue:
score, x , y = heapq.heappop(queue)
if scoure_board[x][y] < score:
continue
scoure_board[x][y] = score
for dx, dy in [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if out_range(nx, ny):
continue
if board[nx][ny] == 0:
continue
if not is_outline(nx, ny, rocks):
continue
\
temp_score = score + 1
if temp_score < scoure_board[nx][ny]:
scoure_board[nx][ny] = temp_score
heapq.heappush(queue, (temp_score, nx, ny))
return scoure_board
코드
import heapq
def fill_outline(board, x1, y1, x2, y2):
for width in range(y1, y2 + 1):
board[x1][width] = 1
board[x2][width] = 1
for height in range(x2, x1 + 1):
board[height][y1] = 1
board[height][y2] = 1
def out_range(x, y):
if x < 0 or x > 100 or y < 0 or y > 100:
return True
return False
def is_outline(x, y, rocks):
for rock in rocks:
y1, x1, y2, x2 = rock
if x2 < x < x1 and y1 < y < y2:
return False
return True
def bfs(board, x, y, rocks):
queue = []
scoure_board = [[987654321] * 101 for _ in range(101)]
heapq.heappush(queue, (0, x, y))
while queue:
score, x , y = heapq.heappop(queue)
if scoure_board[x][y] < score:
continue
scoure_board[x][y] = score
for dx, dy in [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if out_range(nx, ny):
continue
if board[nx][ny] == 0:
continue
if not is_outline(nx, ny, rocks):
continue
temp_score = score + 1
if temp_score < scoure_board[nx][ny]:
scoure_board[nx][ny] = temp_score
heapq.heappush(queue, (temp_score, nx, ny))
return scoure_board
def solution(rectangle, characterX, characterY, itemX, itemY):
answer = 0
board = [[0] * 101 for _ in range(101)]
characterY = 100 - (characterY*2)
characterX = (characterX*2)
itemY = 100 - (itemY*2)
itemX = (itemX*2)
for i in range(len(rectangle)):
rectangle[i][0] = rectangle[i][0]*2
rectangle[i][1] = 100 - (rectangle[i][1]*2)
rectangle[i][2] = rectangle[i][2]*2
rectangle[i][3] = 100 - (rectangle[i][3]*2)
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in rectangle:
fill_outline(board,y1, x1, y2, x2)
scoure_board = bfs(board, characterY, characterX, rectangle)
return int(scoure_board[itemY][itemX]/ 2)
배운점 정리하기
좌표 정규화 과정이 재미있었습니다.
반응형
'개발 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스] 피로도 (0) | 2024.04.21 |
|---|---|
| [프로그래머스] 퍼즐 조각 (1) | 2024.04.16 |
| [프로그래머스] 징검다리 (0) | 2024.04.13 |
| [프로그래머스] H-index (1) | 2024.04.11 |
| [프로그래머스] 등대 (0) | 2024.04.09 |





